Running IESI on Google Cloud Platform
This page describes how to install IESI on the Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and what considerations to take into account when running the solution.
Getting started with a Mark2 deployment
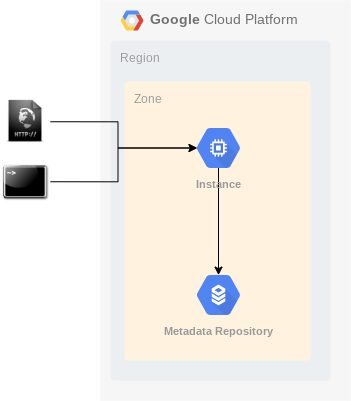
A Mark2 deployment of IESI on GCP consists of two parts: a Compute Engine instance to run the services and a Cloud SQL instance to host the metadata repository.
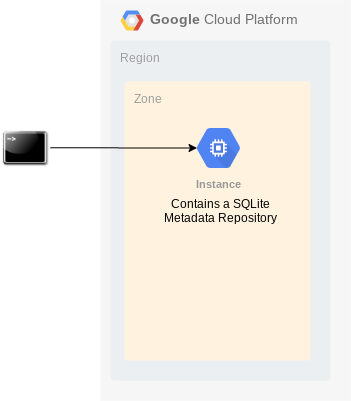
Note: if you would opt for a local SQLite database during a Proof of Concept or a small size project, then you will not need to create the Cloud SQL instance.
As with any GCP solution, you will need to create or select a project where the different resources will run. We will demonstrate the steps to get up and running using a basic setup. Using GCP’s organization and networking capabilities, this can be optimized for your situation or requirements. See here for more information.
In the next steps, we will use the project iesi-01 to deploy resources to. Activate the cloud shell in the console and make sure to set the following configurations:
gcloud config set project [project]
gcloud config set compute/zone [zone]
You are not required to use the command line but can make use of the Google Cloud console which allows to create resources and set options easily using an intuitive user interface.
First, we will create a Compute Engine instance. This will be the virtual machine where the IESI solution will run.
gcloud compute --project=iesi-01 instances create instance-1
This will create a n1-standard-1 instance with a default debian image. This command be extended with additional options as needed, including the project, zone, machine type, … allowing to automate the deployment. More information on these options can be found on the following page.
We have selected the default configuration of cpu and memory. The nice thing about running IESI from GCP is that you will be able to resize this instance as you go. This allows you to grow as more resources are needed. But is also avoids excess cost since you do not need to provision everything from the start.
Important: at this moment, no firewall rules have been defined for the instance, so accessing it through http(s) is not possible yet. So, access to the Rest API server is not possible yet; the appropriate firewall rules need to be added first. You can find more information about firewalls here.
From the console, it is now possible to perform an SSH into instance-1. From this moment, it is possible to take all necessary actions installing the IESI solution.
Next, we will set up a Cloud SQL instance to host the metadata repository. You can choose from MySQL, Postgres and MS SQL Server. Luckily all supported by IESI. The advantage of Cloud SQL is that it is a managed version of these database types, reducing the complexity of installation and maintenance.
gcloud sql instances create repository-1 --database-version=MYSQL_5_7 --root-password=[password] --region=[region] --zone=[zone]
The creation of the instance can be tuned to reflect the installation needs, including database version, high-availability, backup, … More information on these options can be found on the following page.
Now, the Cloud SQL instance is ready to be configured and used.
Connecting the instance with the metadata repository
There are different options to connect the Compute Engine instance to the Cloud SQL instance. You will be able to implement this depending on your organisation or project policies. More information can be found here.
To get started quickly, have a look at the following tutorial.
Once that it is possible to connect from the instance to the metadata repository, you are all set to start the installation process for the IESI solution itself. Have a look at the installation guide for this.
That’s it! You are now ready to run IESI.
Getting started faster for a PoC with a Mark1 deployment
You can get started even faster, for instance when running a proof of concept by using a Mark1 deployment. With limited workloads, a Cloud SQL instance is not required and can be replaced with a local SQLite file based database. So, you only need to provision a compute engine instance and follow the necessary IESI installation steps.